AP Physics 1 Torque and Rotational Motion MCQs delves into the fascinating realm of rotational dynamics, equipping students with a comprehensive understanding of torque, rotational inertia, and their profound impact on the motion of objects. This in-depth exploration of rotational motion unveils the fundamental principles governing the behavior of rotating systems, providing a solid foundation for further studies in physics and engineering.
Through a series of meticulously crafted multiple-choice questions, this resource challenges students to apply their knowledge of torque and rotational motion to real-world scenarios. Each question is designed to test students’ conceptual understanding, analytical skills, and problem-solving abilities, fostering a deeper comprehension of this essential topic.
Torque and Rotational Motion Concepts: Ap Physics 1 Torque And Rotational Motion Mcq
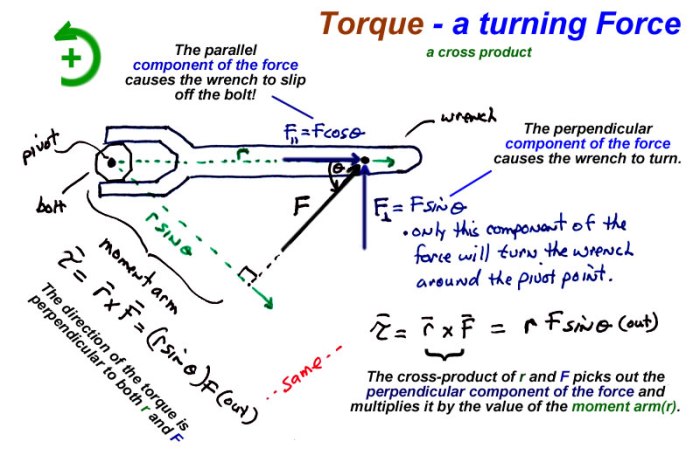
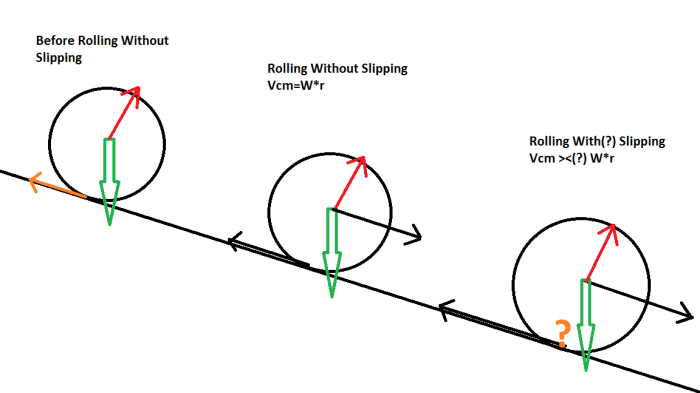
Torque is a force that causes an object to rotate about an axis. It is calculated as the product of the force applied and the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation. Torque is a vector quantity, meaning it has both magnitude and direction.
Factors that affect torque include the magnitude of the force applied, the distance from the axis of rotation, and the angle between the force and the lever arm. Torque is an important concept in rotational motion, as it determines the angular acceleration of an object.
Rotational Inertia
Rotational inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to angular acceleration. It is analogous to mass in linear motion. Factors that affect rotational inertia include the mass of the object, the distribution of mass around the axis of rotation, and the shape of the object.
Rotational inertia is an important concept in rotational motion, as it determines the angular acceleration of an object for a given torque.
Moment of Inertia
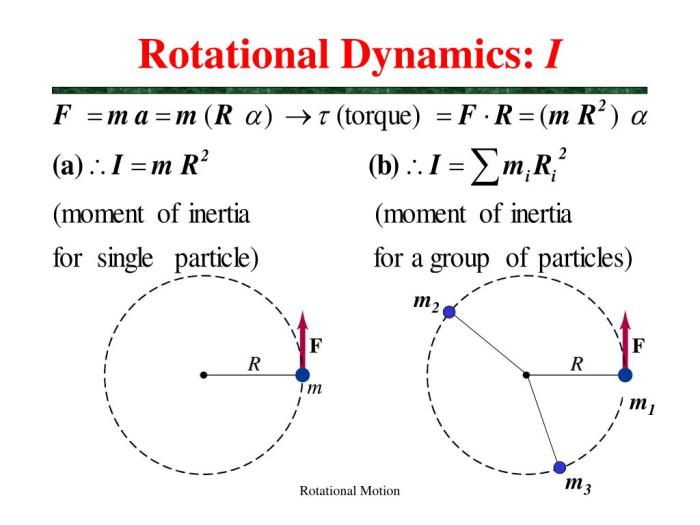
Moment of inertia is a scalar quantity that characterizes the distribution of mass in an object. It is calculated as the sum of the products of each particle’s mass and the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.
Moment of inertia is an important concept in rotational motion, as it is used to calculate the rotational kinetic energy and angular momentum of an object.
Angular Acceleration and Velocity
Angular acceleration is the rate of change of angular velocity. It is calculated as the derivative of angular velocity with respect to time. Angular velocity is the rate of change of angular displacement with respect to time.
Angular acceleration and velocity are important concepts in rotational motion, as they describe the motion of an object rotating about an axis.
Rotational Kinetic Energy, Ap physics 1 torque and rotational motion mcq
Rotational kinetic energy is the energy of an object due to its rotation. It is calculated as the product of the moment of inertia and the square of the angular velocity.
Rotational kinetic energy is an important concept in rotational motion, as it is conserved in the absence of external torque.
Collision in Rotational Motion
Collisions in rotational motion occur when two or more objects rotating about different axes collide. The conservation of angular momentum is an important principle that applies to collisions in rotational motion.
Collisions in rotational motion are important in many applications, such as sports, engineering, and mechanics.
Applications of Torque and Rotational Motion
Torque and rotational motion have a wide range of applications in various fields, including engineering, mechanics, and sports. Some examples include:
- Machines that use gears, pulleys, and levers to transmit and amplify force and motion
- Vehicles that use wheels and axles to convert linear motion into rotational motion
- Sports equipment that uses torque to generate spin, such as baseball bats and golf clubs
Answers to Common Questions
What is torque, and how does it relate to rotational motion?
Torque is a measure of the force that causes an object to rotate. It is calculated by multiplying the force applied to an object by the perpendicular distance from the axis of rotation.
Define rotational inertia and explain its significance in rotational motion.
Rotational inertia is a measure of an object’s resistance to angular acceleration. It depends on the mass of the object and its distribution around the axis of rotation.
What is the relationship between moment of inertia and rotational inertia?
Moment of inertia is a quantity that relates the angular acceleration of an object to the torque applied to it. It is calculated by integrating the mass of the object over the square of its distance from the axis of rotation.